代理模式是一种结构型设计模式,它通过引入“代理对象”来控制原始对象的访问。这个代理对象与我们要访问的原始对象实现相同的接口,然后客户端就可以通过代理对象访问原始对象。那么我们就可以实现在不修改原始对象电的情况下增加额外的功能。比如,实现权限控制、日志记录或者延迟加载等。
下面是一个代理模式的UML类图:
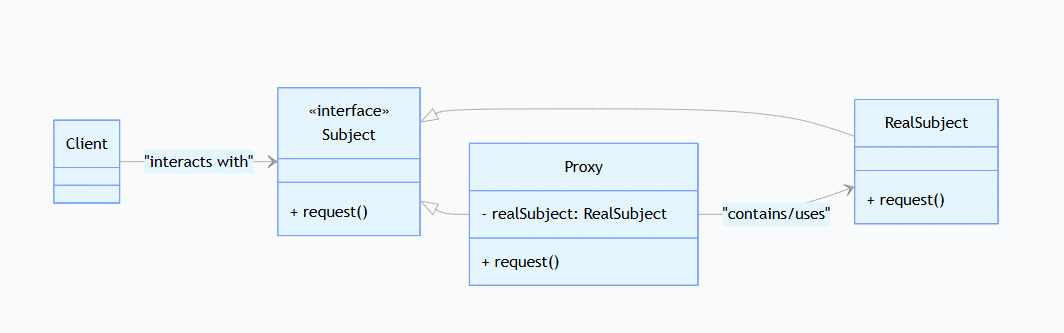
在上面的类图中:
- Subject:是一个抽象主题,它定义了我们真实要访问的主题和代理对象的公共接口,客户端直接和这个接口交互。
- RealSubject: 它是客户端实际上要操作的对象,它也实现了Subject接口。
- Proxy:是代理对象,它实现了Subject的接口,内部持有RealSubjet的引用,它负责控制对真实主体对象的访问,并且还可以增加额外的操作
- Client:是客户端,它只和Subject接口交互,无需知道真实主体的存在。
代理模式的关键是代理对象与真实对象实现相同的接口,从而实现对真实对象的透明访问,同时可以在访问过程中增加额外功能。
举一个具体的例子。比如在分布式系统中,客户端需要调用远程服务器上的服务(如微服务接口),直接调用会涉及网络通信、序列化 / 反序列化等复杂逻辑。使用代理模式可以将这些细节封装在代理对象中,让客户端像调用本地方法一样使用远程服务。
下面的代码模拟了一个电商系统中,客户端需要调用远程库存服务查询商品库存,代理对象负责处理网络通信细节:
首先创建一个代表主题的库存服务接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public interface InventoryService {
int getStock(String productId);
boolean reduceStock(String productId, int quantity);
}
|
然后创建一个代理丢下实现这个接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public class RemoteInventoryProxy implements InventoryService {
@Override
public int getStock(String productId) {
System.out.println("[代理] 开始远程调用:查询库存,商品ID=" + productId);
System.out.println("[代理] 建立网络连接,发送请求...");
InventoryService remoteService = new RemoteInventoryServiceImpl();
int stock = remoteService.getStock(productId);
System.out.println("[代理] 接收响应,关闭连接");
return stock;
}
@Override
public boolean reduceStock(String productId, int quantity) {
System.out.println("[代理] 开始远程调用:扣减库存,商品ID=" + productId + ",数量=" + quantity);
System.out.println("[代理] 建立网络连接,发送请求...");
InventoryService remoteService = new RemoteInventoryServiceImpl();
boolean result = remoteService.reduceStock(productId, quantity);
System.out.println("[代理] 接收响应,关闭连接");
return result;
}
}
|
真实的库存服务对象也实现这个接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public class RemoteInventoryServiceImpl implements InventoryService {
@Override
public int getStock(String productId) {
System.out.println("[服务器] 查询商品 " + productId + " 的库存");
return 150;
}
@Override
public boolean reduceStock(String productId, int quantity) {
System.out.println("[服务器] 扣减商品 " + productId + " 的库存:" + quantity);
return true;
}
}
|
下面的代码演示了客户端调用的方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public class InventoryClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InventoryService inventoryService = new RemoteInventoryProxy();
int stock = inventoryService.getStock("product_123");
System.out.println("商品库存:" + stock);
boolean success = inventoryService.reduceStock("product_123", 10);
System.out.println("扣减库存是否成功:" + success);
}
}
|
代理模式的优势如下:
- 透明访问:客户端无需知道原始对象的存在,代理对象对客户端透明。
- 功能增强:在不修改原始对象的情况下,通过代理添加日志、缓存、权限校验等功能。
- 资源优化:例如使用 “虚拟代理” 延迟加载大对象,只有在真正需要时才初始化。
